We’re happy to announce that we were successfully able to initiate a BusKill lockscreen trigger using a 3D-printed BusKill prototype!
While we do what we can to allow at-risk folks to purchase BusKill cables anonymously, there is always the risk of interdiction.
We don’t consider hologram stickers or tamper-evident tape/crisps/glitter to be sufficient solutions to supply-chain security. Rather, the solution to these attacks is to build open-source, disassembleable, and easily inspectable hardware whose integrity can be validated without damaging the device and without sophisticated technology.
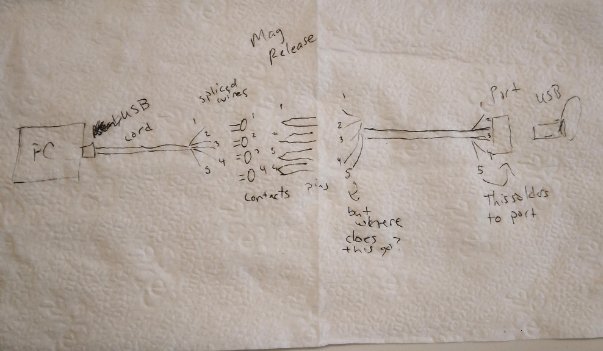
Actually, the best way to confirm the integrity of your hardware is to build it yourself. Fortunately, printing your own circuit boards, microcontroller, or silicon has a steeper learning curve than a BusKill cable — which is essentially just a USB extension cable with a magnetic breakaway in the middle.
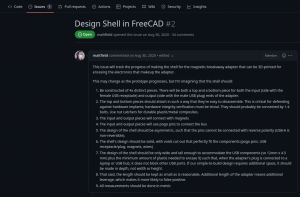
Mitigating interdiction via 3D printing is one of many reasons that Melanie Allen has been diligently working on prototyping a 3D-printable BusKill cable this year. In this article, we hope to showcase her progress and provide you some OpenSCAD and .stl files so you can experiment with building your own and help test and improve our designs.
ⓘ Note: This post is adapted from its original article on Melanie Allen’s blog.
Demo
Last month, I successfully triggered a lockscreen event using our 3D-printed BusKill prototype.